Root Planing and Scaling for Gum Disease
A dental prophylaxis is a cleaning procedure performed to thoroughly clean the teeth. Prophylaxis is an important dental treatment for halting the progression of periodontal disease and gingivitis.
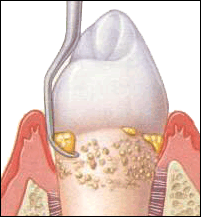
Periodontal disease and gingivitis occur when bacteria from plaque colonize on the gingival (gum) tissue, either above or below the gum line. These bacteria colonies cause serious inflammation and irritation which in turn produce a chronic inflammatory response in the body. As a result, the body begins to systematically destroy gum and bone tissue, making the teeth shift, become unstable, or completely fall out. The pockets between the gums and teeth become deeper and house more bacteria which may travel via the bloodstream and infect other parts of the body.
Reasons for prophylaxis/teeth cleaning
Prophylaxis is an excellent procedure to help keep the oral cavity in good health and also halt the progression of gum disease.
Here are some of the benefits of prophylaxis:
-
Tartar removal – Tartar (calculus) and plaque buildup, both above and below the gum line, can cause serious periodontal problems if left untreated. Even using the best brushing and flossing homecare techniques, it can be impossible to remove debris, bacteria and deposits from gum pockets. The experienced eye of a dentist using specialized dental equipment is needed in order to spot and treat problems such as tartar and plaque buildup.
-
Aesthetics – It’s hard to feel confident about a smile marred by yellowing, stained teeth. Prophylaxis can rid the teeth of unsightly stains and return the smile to its former glory.
-
Fresher breath – Periodontal disease is often signified by persistent bad breath (halitosis). Bad breath is generally caused by a combination of rotting food particles below the gum line, possible gangrene stemming from gum infection, and periodontal problems. The removal of plaque, calculus and bacteria noticeably improves breath and alleviates irritation.
Identification of health issues – Many health problems first present themselves to the dentist. Since prophylaxis involves a thorough examination of the entire oral cavity, the dentist is able to screen for oral cancer, evaluate the risk of periodontitis and often spot signs of medical problems like diabetes and kidney problems. Recommendations can also be provided for altering the home care regimen.
What does prophylaxis treatment involve?
Prophylaxis can either be performed in the course of a regular dental visit or, if necessary, under general anesthetic. The latter is particularly common where severe periodontal disease is suspected or has been diagnosed by the dentist. An endotracheal tube is sometimes placed in the throat to protect the lungs from harmful bacteria which will be removed from the mouth.
Prophylaxis is generally performed in several stages:
-
Supragingival cleaning – The dentist will thoroughly clean the area above the gum line with scaling tools to rid them of plaque and calculus.
-
Subgingival cleaning – This is the most important step for patients with periodontal disease because the dentist is able to remove calculus from the gum pockets and beneath the gum line.
-
Root planing - This is the smoothing of the tooth root by the dentist to eliminate any remaining bacteria. These bacteria are extremely dangerous to periodontitis sufferers, so eliminating them is one of the top priorities of the dentist.
-
Medication - Following scaling and root planing, an antibiotic or antimicrobial cream is often placed in the gum pockets. These creams promote fast and healthy healing in the pockets and help ease discomfort.
-
X-ray and examination – Routine X-rays can be extremely revealing when it comes to periodontal disease. X-rays show the extent of bone and gum recession, and also aid the dentist in identifying areas which may need future attention.
Prophylaxis is recommended twice annually as a preventative measure, but should be performed every 3-4 months on periodontitis sufferers. Though gum disease cannot be completely reversed, prophylaxis is one of the tools the dentist can use to effectively halt its destructive progress.
If you have questions or concerns about prophylaxis or periodontal disease, please ask your dentist.
Root planing and scaling is one of the most effective ways to treat gum disease before it becomes severe. Root planing and scaling cleans between the gums and the teeth down to the roots. Your dentist may need to use a local anesthetic to numb your gums and the roots of your teeth. Some dentists and dental hygienists will use an ultrasonic tool for the planing and scaling. This tool is not as uncomfortable as a standard scraping tool, but not all cleanings require this type of tool.
Your dentist may place antibiotic fibers into the pockets between your teeth and gums. The antibiotic will help speed healing and prevent infection. The dentist will remove the fibers about 1 week after the procedure.
What To Expect After Treatment
If anesthesia is used, your lips and gums may remain numb for a few hours. Planing and scaling causes little or no discomfort. Why It Is Done Root planing and scaling is done when gums have either started to pull away from the teeth or the roots of the teeth have hard mineral deposits (tartar) on them. How Well It Works If you maintain good dental care after the procedure, the progression of gum disease should stop. And your gums will heal and become firm and pink again.